To stop a simulation at a specified time, try the following script.
Open the terminal window by clicking the “terminal” checkbox.
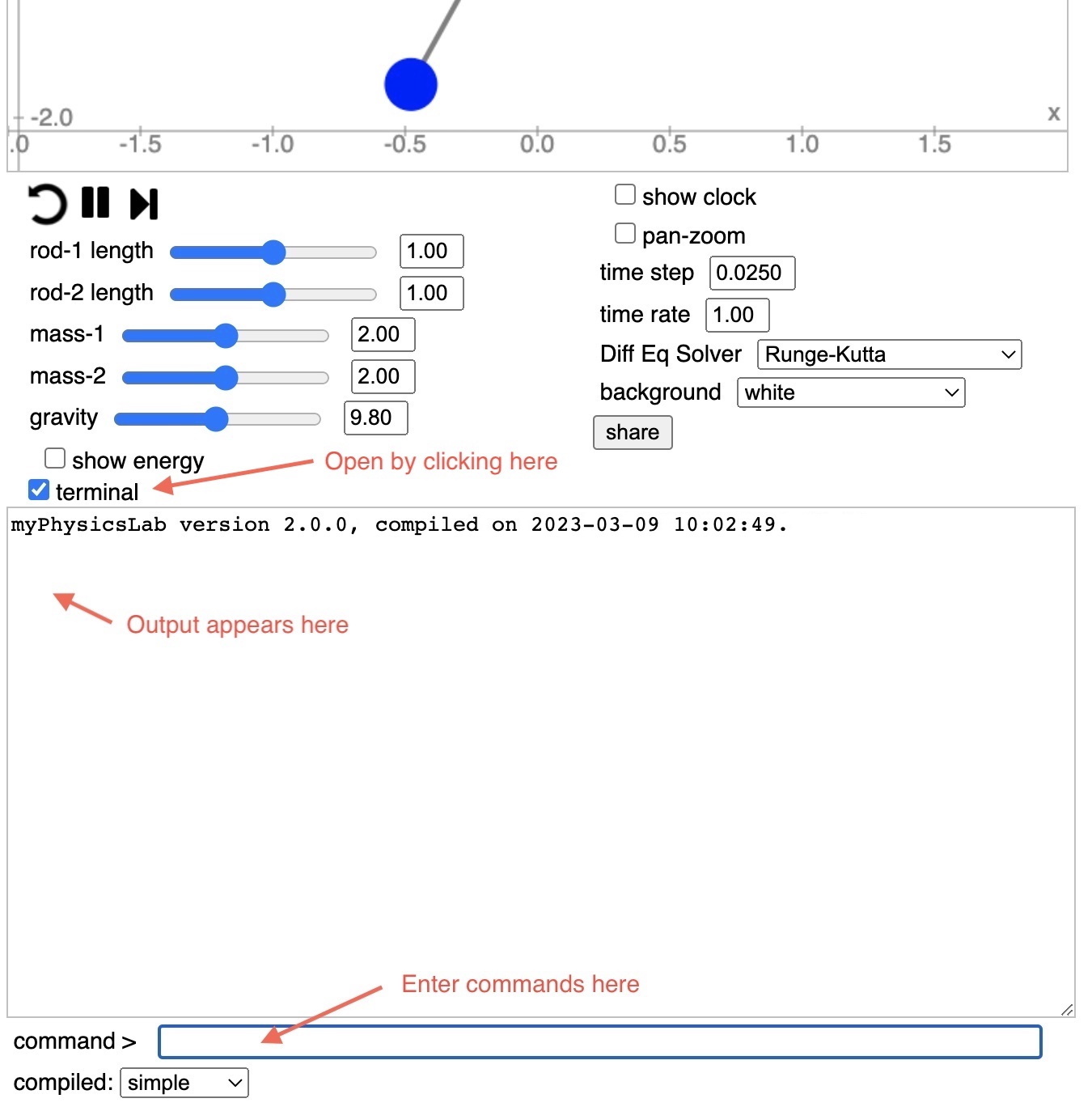
Type help in the command box (and hit return of course) to see available Terminal
commands.
Set your desired initial conditions on the simulation.
Paste into the Terminal command box this script
var stopTime = 1.99;
var memo = new GenericMemo(function(){
if (sim.getTime()>=stopTime) { simRun.pause() }
});
simRun.addMemo(memo);
To see it working try this link (hit “play” after it loads).
Check that time is set to zero by typing time or sim.getTime() in the Terminal
command box. If time is not zero, click the reset button or execute the reset command.
Start the simulation running, it will stop once the time exceeds the stopTime.
To continue running the simulation after it stops:
set the stopTime to a later time, for example stopTime = 3.99 and execute resume
(or click the “play” button). Otherwise, whenever you resume the simulation, the
memo immediately stops it.
or execute simRun.removeMemo(memo) in the Terminal command box
Explanation of things in the script:
A GenericMemo is called whenever the
simulation steps forward in time. Therefore the
only way to cancel it is to remove it, or change its stopTime to far in the future.
The simRun variable is an instance of
SimRunner which controls the advancement of
the simulation over time.
The sim variable is an instance of whichever simulation is running,
such as DoublePenduluml.
Similar techniques can be used to stop the simulation based on other conditions. For example, to stop the simulation when the energy drops below a certain value.
Determine which variable holds the energy.
Find the names of the variables by typing names into the Terminal command box. For the
Pendulum
simulation you would see a list ending with this
SIM_VARS.ANGLE;
SIM_VARS.ANGLE_VELOCITY;
SIM_VARS.TIME;
SIM_VARS.ANGLE_ACCELERATION;
SIM_VARS.KINETIC_ENERGY;
SIM_VARS.POTENTIAL_ENERGY;
SIM_VARS.TOTAL_ENERGY
Enter the following script into the Terminal command box. (You can copy and paste all the lines at once.)
var energyVar = sim.getVarsList().getVariable('TOTAL_ENERGY');
var energyLimit = 0.1;
var memo = new GenericMemo(function(){
if (energyVar.getValue() < energyLimit) { simRun.pause()}
});
simRun.addMemo(memo);
To see it working try this link (hit “play” after it loads).
Check that time time is set to zero by typing time or sim.getTime() in the Terminal command box. If time is not zero, click the reset button or execute the reset command.
Start the simulation running, it will stop once the total energy drops below energyLimit.
To continue running the simulation after it stops:
energyLimit to a lower value, for example energyLimit = 0.01simRun.removeMemo(memo) in the Terminal command boxHere are some other tasks that can be triggered by various events.
Change the time rate of the clock to slow down or speed up at a certain
time. See the setTimeRate method of
Clock.
Print information when certain events happen using the println command
which is available in Terminal. For
example, when an object’s position crosses a certain line you can print the time
and other variables.
Cause a simulation to loop, going back to time zero, by executing
simRun.reset() at a certain time. See the reset method of
SimRunner.
Change a parameter like gravity or damping at a certain time.
Another way to stop a simulation at a certain time is to create a ClockTask and add it to a Clock. For example, this script stops the simulation after 2 seconds.
var task = new ClockTask(2, () => simRun.pause());
clock.addTask(task);
A ClockTask is executed only once when the time on the clock reaches the scheduled time for the task. After the task stops the simulation at 2 seconds, you could hit “play” and the simulation would continue.
But if you rewind (reset) the simulation to time zero, the ClockTask is still active and will again stop the simulation at 2 seconds. You can cancel the task with
clock.removeTask(task);
Here is a ClockTask that restarts the simulation every 2 seconds.
var task = () => simRun.reset();
clock.addTask(new ClockTask(2, task));
Here is a ClockTask that slows the time rate the Clock after 2 seconds:
var task = new ClockTask(2, () => clock.setTimeRate(0.1));
clock.addTask(task);
Another way to execute a script is by making a GenericObserver that looks for certain events to occur.
Suppose you have installed one of the above scripts that slows the time rate of the Clock. You run the simulation, and it slows down. But now you want to try it again. It’s annoying to need to manually reset the time rate to 1 every time. Here is a script that does that automatically whenever you hit the rewind (reset) button.
var obs = new GenericObserver(simRun, evt => {
if (evt.nameEquals('RESET')) {
clock.setTimeRate(1);
}
});
Whenever the GenericObserver sees a RESET event on the SimRunner, it sets the time rate on the clock.
There are many Events being broadcast by various objects all the time. For example a Clock broadcasts whenever it starts or stops (pause or resume). See the section about Subject-Observer in the Architecture overview.